Units For Specific Heat
Units For Specific Heat. Specific heat , the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one celsius degree. It may also be expressed as j/kg·k.
It is in the form of heat or light or light, both types of energy are crucial to life. The method of transfer of heat between one object and another depends on the kind of material that the object is constructed of as well as the conditions in that it's placed. The principal forms of heat transfer include convection (radiation) as well as convection (energy transfer) and convection (convection).
Transfer of energyEnergy transfer, in general is the exchange or movement of energy between two or more entities. You can transfer energy from one store to the next or one object to the other. Energy can be transferred from one store to another or from one thing to another for many reasons. This process is crucial for all life on Earth.
Two ways energy can be transferred are through conduction and radiation. Conduction, a powerful method for heat transfer in metallic materials is extremely efficient. For instance, a spoon is able to conduct heat effectively and, when it is placed in water that is hot, the spoon handle will become hot.
Radiation is a major method of heat transfer, and is essential for life on Earth. If a fire starts to rage huge quantities of energy are transferred into the air. This accelerates its speed. The energy is able to travel in all directions.
Latent and sensible heatEnergy travels through space no matter whether it is either sensual or latent heat. It is dependent on the temperature of air. It can happen through direct conduction, or the transfer of energy from one substance to another. This is the most famous example of energy required to raise or lower water temperature.
The energy required to make the change in phase of an element is known as sensible heat. There are many situations where sensible heat may be needed, such cooling or heating water.
Two of the most crucial elements of the climate system are sensual heat as well as latent heat. They are essential in climate, weather oceanic, as well as other processes.
The presence of water vapor and air in the air can help to release both sensitive and latent heat. Water vapor is a greenhouse gas that is a key element in cloud formation. The atmosphere is filled with water vapor and wants to rise to create clouds. When the atmosphere is not dry enough to hold water vapor, the heat in the vapor is absorbed.
ConductionConduction is the process of heat transfer. Conduction is a method used to transfer heat.
Conduction can be defined as the process of transferring heat across the solid, liquid or gas. It is influenced by temperature, distance traveled and the properties of the material. Conduction is determined by thermal conductivity. It is the process of transferring heat energy through a substance. The thermal conductivity can be measured in W m-1K-1 units.
The speed at which electrons travel from one atom to another is what determines the material's thermal conductivity. It also tells how the substance is able to transfer energy. The thermal conductivity is a measurement of how well objects can take on heat. objects with low thermal conductivity can be considered to be insulators.
ConvectionConvection is an efficient way to heat and cool. Convection heat transfer is dependent on various factors, such as the form of the fluid and the speed of flow. It is important to be aware that the rate of convection heating transfer is proportional with the fluid's initial and final temperatures.
First law of thermodynamics says that heat loss is proportional to temperature. A hot object loses heat more quickly than an object that is cold. This can be seen in the following example The glass you've put in of hot water with red food coloring in a tank for fish. When the water cools, the dye will become solid and the liquid will become transparent.
RadiationRadiation can be seen in the form of heat, light, or both. In its most basic form, thermal radiation is the release of heat by particles of matter in the form of cold or heat. The electromagnetic radiation that is produced by thermal radiation appears as waves in its highest form. In certain instances, the wavelength of thermal radiation is related to the temperature at which it occurs. Radiation that is related to heat is the most prevalent in the infrared spectrum. An infrared camera can capture it. You can also infuse it by conduction of heat. This is also a sign of heat-related chemistry.
The best way to understand the magnitude of thermal radiation is to think of its spectral components in the context of the overall volume of the matter. It is black holes if it doesn't have the same volume.
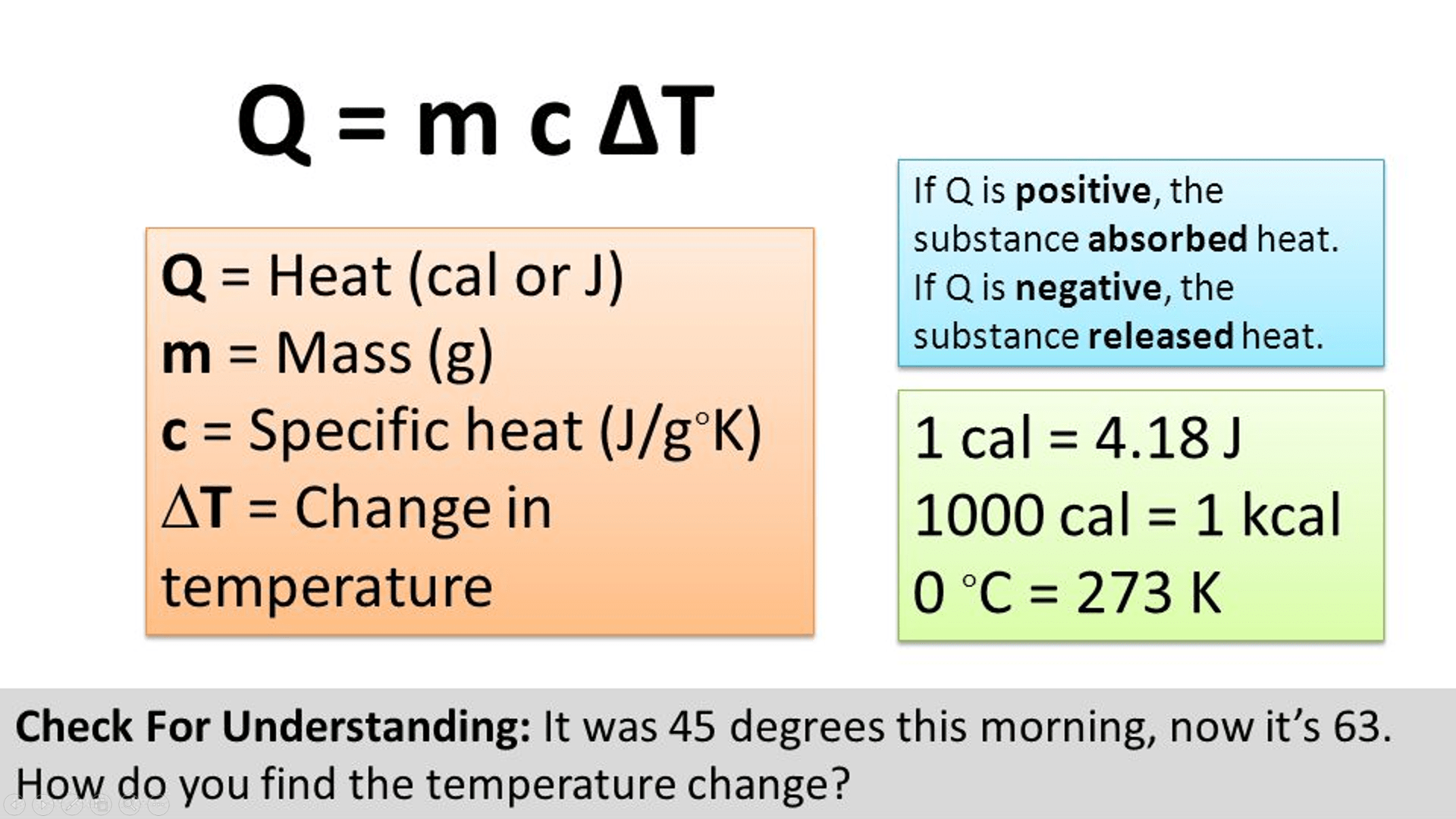
In si units, specific heat capacity (symbol: Definition of specific heat capacity revealed that it is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kilogram of any substance by 1 kelvin. Each substance has their own specific heat capacity,.
Definition Of Specific Heat Capacity Revealed That It Is The Amount Of Heat Required To Increase The Temperature Of 1 Kilogram Of Any Substance By 1 Kelvin.
It may also be expressed as j/kg·k. Unit of specific heat capacity is j k g − 1 k − 1 specific heat capacity of water, ice, copper specific heat capacity of water at normal. How to calculate specific heat step 1:
Specific Heat Capacity, C = Q M ∆ T, Where M Is The Mass Of Substance, Q Is Heat Absorbed, And ∆ T Is The Change In Temperature.
Specific heat , the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one celsius degree. Specific heat capacity units the s.i. It is denoted by c or s.
55 Rows Heat Capacity C P J⋅G −1 ⋅K −1 Isobaric Molar Heat Capacity C P,M J⋅Mol −1 ⋅K −1 Isochore Molar Heat Capacity C V,M J⋅Mol −1 ⋅K −1 Isobaric Volumetric Heat Capacity C P,V.
The si unit for specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram j/kg⋅k, j⋅k ⋅kg. Since an increment of temperature of one degree celsius is the same as an increment of one kelvin, that is the same as joule per degree celsius per kilogram: Joule is the si unit of heat.
Sometimes The Gram Is Used Instead Of Kilogram For The Unit Of Mass:
The specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat (j) absorbed per unit mass (kg) of the material when its temperature increases 1 k (or 1 °c), and its units are j/(kg k) or j/(kg °c). Convert the heat energy to units of jules [j]. C) is the amount of heat in joules required to raise 1 gram of a substance 1 kelvin.
1 J⋅G ⋅K = 0.001 J⋅Kg ⋅K.
The specific heat capacity of a substance (per unit of mass) has dimension l ⋅θ ⋅t , or (l/t) /θ. Si unit of specific heat capacity it is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kg of liquid or solid by 1 k in si units. Calculate the temperature difference by.
Post a Comment for "Units For Specific Heat"